Energy Monitoring: A Key Tool for Efficiency and Sustainability
Introduction
In today’s world, with the growing population and increasing demand for energy, energy management and optimization have become essential. Energy monitoring, as a powerful tool, plays a key role in this area.
Definition of Energy Monitoring
Energy monitoring is the process of collecting, analyzing, and reporting data related to energy consumption in a system or facility. This process can include measuring and monitoring the consumption of electricity, water, gas, and other energy sources.
Benefits of Energy Monitoring
There are many benefits to energy monitoring, including:
- Cost reduction: By identifying and correcting inefficient consumption patterns, energy costs can be significantly reduced.
- Increased efficiency: Energy monitoring helps identify weaknesses and inefficiencies in energy systems, paving the way for efficiency upgrades and performance improvements.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: By optimizing energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions and their harmful environmental impacts can be reduced.
- Increased transparency: Energy monitoring provides users with transparent information on how and how much energy is being consumed, helping them make informed decisions and optimize consumption.
- Improved energy management: Energy monitoring provides the necessary information for better planning and management of energy resources.
Applications of Energy Monitoring
Energy monitoring can be applied in various sectors, including:
- Buildings: Energy monitoring can be used to track energy consumption in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. This information can be used to identify areas for improvement and implement energy-saving measures.
- Industry: Energy monitoring can be used to track energy consumption in manufacturing and processing facilities. This information can be used to optimize energy use and reduce production costs.
- Utilities: Energy monitoring can be used to track energy consumption in power grids and distribution networks. This information can be used to improve grid efficiency and reduce energy losses.
- Transportation: Energy monitoring can be used to track energy consumption in vehicles and transportation systems. This information can be used to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Technologies for Energy Monitoring
There are a variety of technologies available for energy monitoring, including:
- Smart meters: Smart meters can be used to collect real-time data on energy consumption. This data can be used to monitor energy use and identify areas for improvement.
- Sensors: Sensors can be used to collect data on various energy parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate. This data can be used to monitor energy use and optimize energy systems.
- Data analytics: Data analytics can be used to analyze energy data and identify patterns and trends. This information can be used to improve energy efficiency and reduce costs.
Conclusion
Energy monitoring is a powerful tool that can be used to improve energy efficiency, reduce costs, and protect the environment. With the increasing availability of technologies and the growing awareness of the importance of energy management, energy monitoring is becoming an essential part of modern energy systems.
Additional Information
Energy Efficiency Measures
There are a wide range of energy efficiency measures that can be implemented in buildings, industries, and transportation systems. Some of the most common measures include:
- Upgrading to energy-efficient appliances and equipment: Replacing old, inefficient appliances and equipment with new, energy-efficient models can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Improving insulation: Adding insulation to buildings and pipes can help reduce heat loss and save energy.
- Adopting energy-efficient practices: Making simple changes to energy-use habits, such as turning off lights when not in use and unplugging electronics when not in use, can also contribute to energy savings.
Energy Efficiency Incentives
Many governments and utilities offer incentives to encourage businesses and individuals to adopt energy efficiency measures. These incentives can include rebates, tax credits, and grants.
By utilizing energy monitoring and implementing energy efficiency measures, we can make significant progress towards achieving a more sustainable and efficient energy future.

Energy Monitoring Methods: A Guide to Efficient and Sustainable Energy Use
Introduction
In today’s world, with rising energy costs and increasing concerns about environmental sustainability, effective energy management has become a critical priority. Energy monitoring plays a pivotal role in this endeavor by providing valuable insights into energy consumption patterns and enabling targeted interventions for optimization.
What is Energy Monitoring?
Energy monitoring is the systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and reporting data on energy consumption in a facility, system, or process. It involves measuring and tracking the usage of various energy sources, such as electricity, water, gas, and fuel, to identify areas of inefficiency and potential savings.
Benefits of Energy Monitoring
The benefits of energy monitoring are numerous and far-reaching, including:
- Cost reduction: By identifying and addressing wasteful consumption patterns, energy monitoring can lead to significant reductions in energy costs.
- Increased efficiency: By pinpointing inefficiencies and weak points in energy systems, energy monitoring facilitates targeted improvements and upgrades, resulting in enhanced operational efficiency.
- Reduced environmental impact: By optimizing energy use, energy monitoring helps curtail greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental pollutants, contributing to a more sustainable future.
- Enhanced transparency: Energy monitoring empowers users with clear and accurate information on their energy consumption patterns, enabling informed decision-making and responsible energy management.
- Improved data-driven decision making: By collecting and analyzing energy data, organizations can make informed decisions about energy procurement, infrastructure investments, and operational strategies.
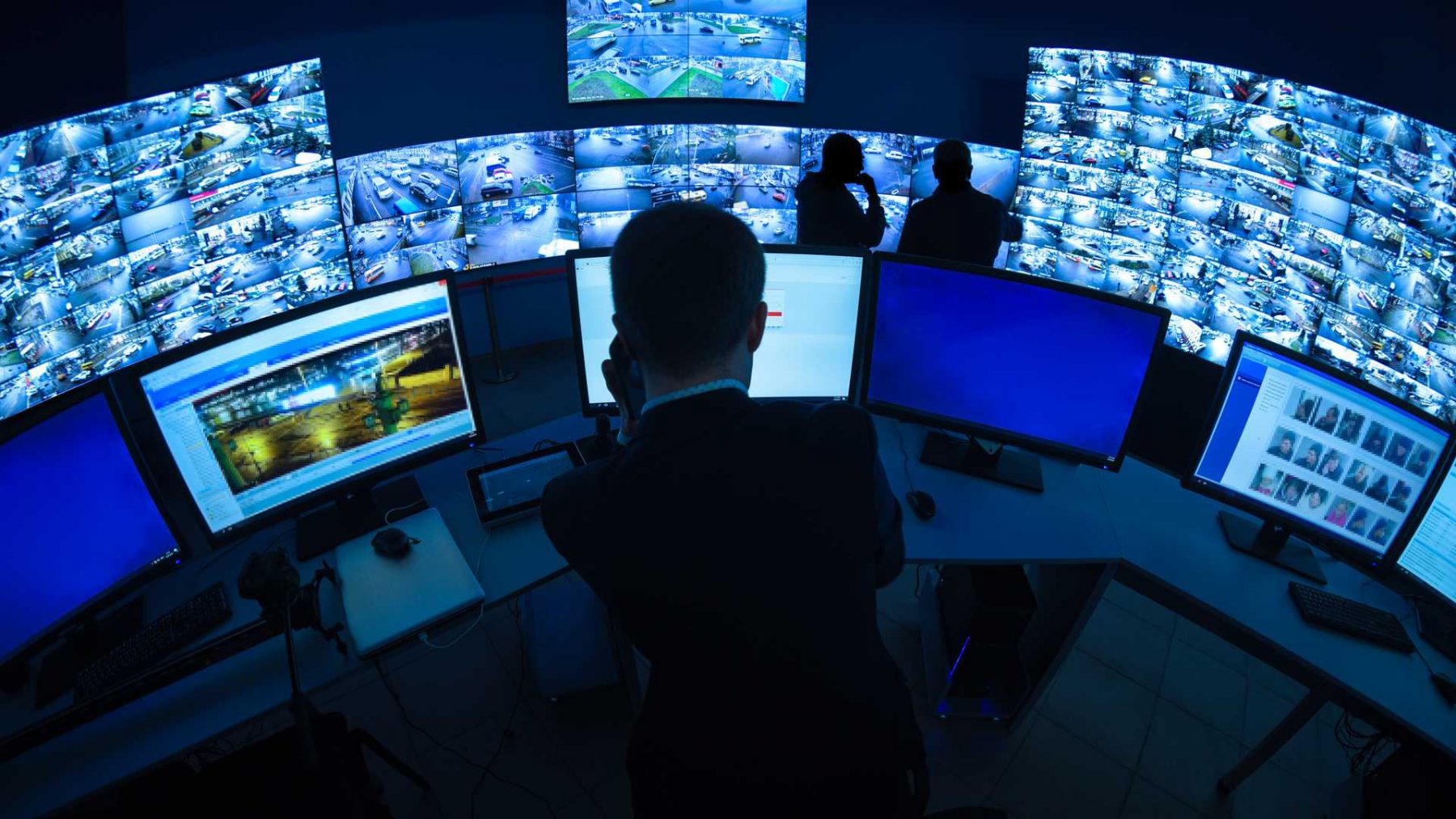
Methods of Energy Monitoring
The choice of an appropriate energy monitoring method depends on various factors, including the type of facility or system, its size and complexity, the desired level of accuracy, and the available budget. Some commonly used methods include:
- Smart meters: These advanced devices collect real-time or interval data on energy consumption, providing a granular view of usage patterns and enabling timely interventions.
- Monitoring systems: These comprehensive solutions employ sensors and other devices to collect data on various energy parameters, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and power consumption. The collected data is then analyzed and presented in user-friendly dashboards and reports.
- Software solutions: Dedicated software platforms are available to facilitate data analysis, visualization, and reporting. These tools empower users to extract meaningful insights from their energy data, identify trends and anomalies, and track progress over time.
Applications of Energy Monitoring
Energy monitoring finds application in a wide range of sectors, including:
- Residential: Homeowners can leverage energy monitoring to understand their energy consumption habits, identify areas of waste, and implement energy-saving measures to reduce their energy bills and environmental impact.
- Commercial and industrial: Businesses and industries can utilize energy monitoring to optimize energy use across their facilities, equipment, and processes. This can lead to significant cost savings, improved productivity, and enhanced environmental performance.
- Utilities: Energy providers can employ energy monitoring to improve grid efficiency, reduce losses, and optimize energy distribution and delivery.
- Transportation: The transportation sector can benefit from energy monitoring by tracking fuel consumption, optimizing fleet operations, and promoting the use of energy-efficient vehicles.
Challenges of Energy Monitoring
While energy monitoring offers a multitude of benefits, it also presents certain challenges that need to be addressed for successful implementation. Some of these challenges include:
- Initial investment: The cost of installing and maintaining energy monitoring systems can be a barrier for some organizations, particularly small businesses and households.
- Data complexity: Dealing with large volumes of data collected from various sources can be challenging, requiring specialized skills and expertise for analysis and interpretation.
- Data security: Ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive energy data is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and potential misuse.
- Behavioral change: Encouraging users to adopt energy-efficient practices and behaviors is essential to maximize the benefits of energy monitoring.
Key Considerations for Effective Energy Monitoring
To ensure successful implementation and maximize the benefits of energy monitoring, organizations should consider the following key factors:
- Selecting the right method: Choosing the appropriate method for energy monitoring based on the specific needs and requirements of the facility or system is crucial.
- Data accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of collected data is essential for making informed decisions and achieving meaningful results.
- Data analysis and interpretation: Investing in robust data analysis tools and skilled personnel to extract valuable insights from the collected data is essential.
- Utilizing appropriate tools and technologies: A wide range of tools and technologies are available to support energy monitoring, and selecting the right ones based on specific needs and budget is crucial.
- Education and awareness: Educating users about energy monitoring and its benefits, as well as providing training on how to use the tools and technologies effectively, is essential for promoting behavioral change and achieving long-term success.
Conclusion
Energy monitoring is a powerful tool that empowers organizations and individuals to take control of their energy consumption, optimize energy use, reduce costs, and